Drug Antibody Ratio.
Drug-Antibody Ratio Analysis is typically performed using Mass Spectrometry, both in the protein engineering stage, in drug substance characterization and in production.
How Drug Antibody Ratio Analysis Works.
An Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) comprises an antibody, a linker and a payload. The payload (or drug load) is typically a small molecule or other cytotoxic agents. ADC have an advantage over small molecule drugs, since they can be highly toxic and specific to the target – hence their development in cancer treatments. The drug antibody ratio calculation is performed after liquid chromatography coupled mass spectrometry (LC-MS). The mass spectrometric analysis calculates the peak area corresponding to the expected mass of the conjugated and non-conjugated forms. Comparing these peak areas reveals the ADC drug antibody ratio. The analysis can be performed on the whole ADC molecule, at the subunit level (e.g. the Fc), or at the peptide level (e.g. the specific conjugation site).
DAR analysis of the whole molecule
This is the simplest workflow, and can consider conjugation that happens on the whole molecule. First the sample will be deglycosylated using PNGase, and then sent directly to LC-MS.
DAR analysis using subunits
This ‘middle down’ approach allows for higher resolution, higher sensitivity and a more detailed result. The sample is first deglycosylated, then digested with ides and/or reduced with DDT to three subunits of approximately 25 kDa each – the Fc, Fd and light chain (see figure 1). These are separated by liquid chromatography and analyzed by mass spectrometry.
ADC conjugation site analysis
This ‘bottom up’ approach provides in depth analysis of where the conjugation occurs and to what extent. The sample is usually digested with trypsin and/or chymotrypsin (other enzymes may be used depending on the sequence and conjugation site) and the resulting peptides are sent to LC-MS. Site specific and conjugated peptides are considered for DAR – drug antibody ratio calculations.
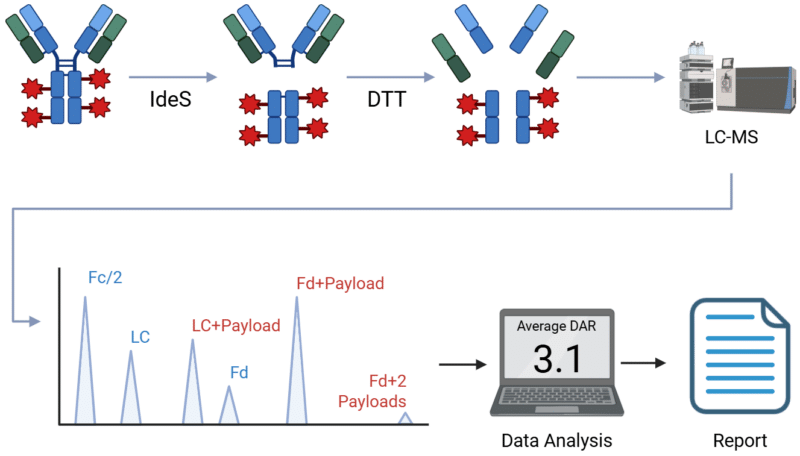
Figure 1
DAR Analysis by Subunit, digestion and reduction followed by LC-MS and data analysis.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 10,000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and developed the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics.
Why DAR Analysis Matters.
Safety is the primary concern with antibody-drug conjugation. Considering the payload has (or can induce) toxic effects intended for the target, it is important that this drug load be conjugated to the antibody and therefore delivered only to the target. Similarly, it is important that the antibodies are sufficiently conjugated in order to have a therapeutic effect. The effects of unintentional or incomplete conjugation can have drastic efficacy and safety repercussions. Engineers and Developers of ADC need to design, measure and maintain a consistent DAR throughout drug design, pre-production, production, preclinical studies and clinical trials.
Tailored design of a DAR analysis.
Not all ADC are designed the same way, so the DAR analysis study must be tailored to the design. The following factors should be considered:
- The intended drug-antibody ratio may be very high or very low
- The antibody may be an engineered format or fragment
- The design may be a single or dual payload
- The conjugation chemistry may rely on different amino acids (e.g. cystine, lysine)
- Glycosylation/deglycosylation may affect ADC conjugation stability
Getting Started.
Requirements
- Antibody Amino acid sequence(s) in FASTA format
- 50 μg of the ADC sample per analysis
- >90% purity
- Antibody must be monoclonal, and the format (e.g. IgG, fragment, bispecific) must be disclosed
- Expected conjugation site and ratio
- Conjugation mechanism (e.g. cysteine conjugated)
- Payload-linker information with chemical formula, molecular weight (exact monoisotopic mass and average mass)
- Any known glycan structure and affect of glycosylation/deglycosylation on the conjugation stability
Deliverables
For an intact or subunit analysis the report will contain:
- MS Spectrum
- Deconvoluted MS Spectrum
- Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) value
- Analysis Report
For ADC conjugation site analysis the report will contain:
- MS Evidence of drug conjugated peptides showing the modification site
- % of conjugation based on the MS signal of modified and unmodified peptides
Timeline
Conjugation Site Analysis
The Science of LC-MS Antibody Characterization.
Antibody Sequencing & Discovery Services.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 9000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics
Talk to our scientists. We have sequenced over 9000+ antibodies and we are eager to help you.
Other Antibody Characterization Services.
Peptide Mapping
Match the masses of individual peptides to the expected masses from a given sequence, maximizing sequence coverage and confidence.
Explore our LC-MS Peptide Mapping Service
Intact Mass Analysis
Determine the mass of the whole antibody or its sub-units to explore a variety of characterization applications.
Explore our Antibody Intact Mass Analysis Service
Glycosylation Analysis
Find glycosylation site occupancy, and profile their relative abundance %. Compare many samples.
Explore our Glycosylation Analysis LC-MS Service
Rapid PTM Analysis
Locate, identify and quantify post-translational modifications. Compare between samples.
Explore our PTM Analysis LC-MS Service
Sequence Variant Assessment
Identify and quantify variants of your intended antibody within your sample, and consider other contaminants.
Explore our SVA Analysis LC-MS Service
Disulfide Bond Analyses
Analyse peptides cross linked by disulfide bonds. Quantify disulfide bond shuffling in engineered constructs.
Explore our Disulfide Bond Analysis LC-MS Service
DAR Analysis
Determine the ratio of antibody to payload in ADC development.
Explore our Drug-Antibody Ratio Analysis Service