Teresa Nunez de Villavicencio Diaz, Chelsea Reitzel, Ming Zhu, Kyle Suttill, Thierry Le Bihan, Bin Ma
Rapid Novor Inc., Kitchener, ON, Canada
Introduction
Anti-idiotype antibodies bind to the variable regions of therapeutic antibodies, mimicking antigens and modulating immune responses. This makes them valuable tools for both vaccine and therapeutic development, for example, as positive controls in Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) studies. The main challenge lies in finding anti-idiotypic antibodies that are highly specific to the therapeutic antibody without cross-reacting with naturally circulating IgGs. Our workflow uses advanced protein enrichment and depletion strategies to isolate functional anti-idiotype subtypes prior to sequencing, significantly improving discovery efficiency.
Using adalimumab as a model, our selection strategies generated a high-performing, anti-idiotype-specific polyclonal antibody (pAb) that outperformed commercially available anti-adalimumab reagents. This pAb was then used in REpAb® antibody discovery, applying mass spectrometry-based sequencing and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to identify and sequence anti-idiotype mAb binders.
A test-then-express approach eliminates non-specific binders early in the workflow, saving time and increasing the likelihood of identifying true functional hits.
Key Takeaways
- Our adalimumab anti-idiotype enrichment strategy yielded a polyclonal antibody (PD182) with less off-target affinity for human IgG than commercially available anti-idiotypes.
- REpAb® antibody sequencing and NGS analysis identified 25 unique heavy chains, 42 kappa light chains and 97 heavy-light chain pairs. The top 30 were produced and tested.
- Recombinantly expressed antibodies demonstrated high affinity for adalimumab with minimal off-target binding to human IgG – only one mAb showed notable cross-reactivity.
Methods
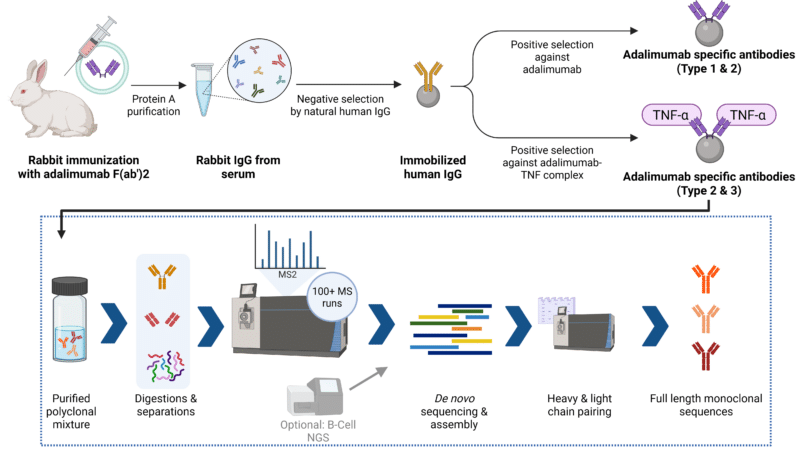
Figure 1: Anti-idiotype antibodies were raised against adalimumab F(ab’)₂ via rabbit immunization with one prime and three boosters. RNA from splenocytes was used for BCR sequencing on an Illumina MiSeq. Proteomic analysis involved native PAGE, IEF, and 2D electrophoresis, followed by in-gel and multi-enzyme in-solution digestion. LC-MS/MS was performed on an Orbitrap Exploris 240 using HCD fragmentation.
Results

Figure 2: ELISA measuring anti-idiotype binding to human IgG was used to assess non-specific interactions. The in-house anti-idiotype PD182 showed lower non-specific binding compared to a commercially available anti-idiotype, demonstrating the specificity gained through our enrichment strategy. Background absorbance was subtracted from all samples.
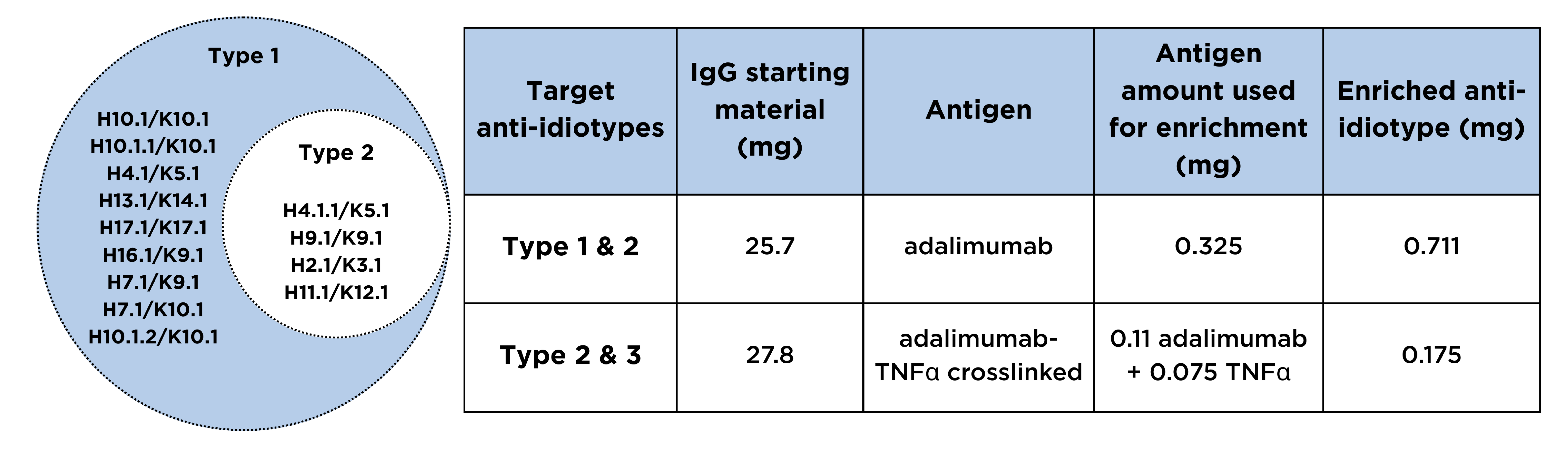
Figure 3: Venn diagram illustrating predicted type 1 and type 2 recombinant anti-idiotypes based on the enrichment fractions in which their sequences were identified. Type 1 anti-idiotypes were detected in the adalimumab enrichment only, while type 2 anti-idiotypes were present in both the adalimumab and adalimumab–TNFα crosslinked enrichments.
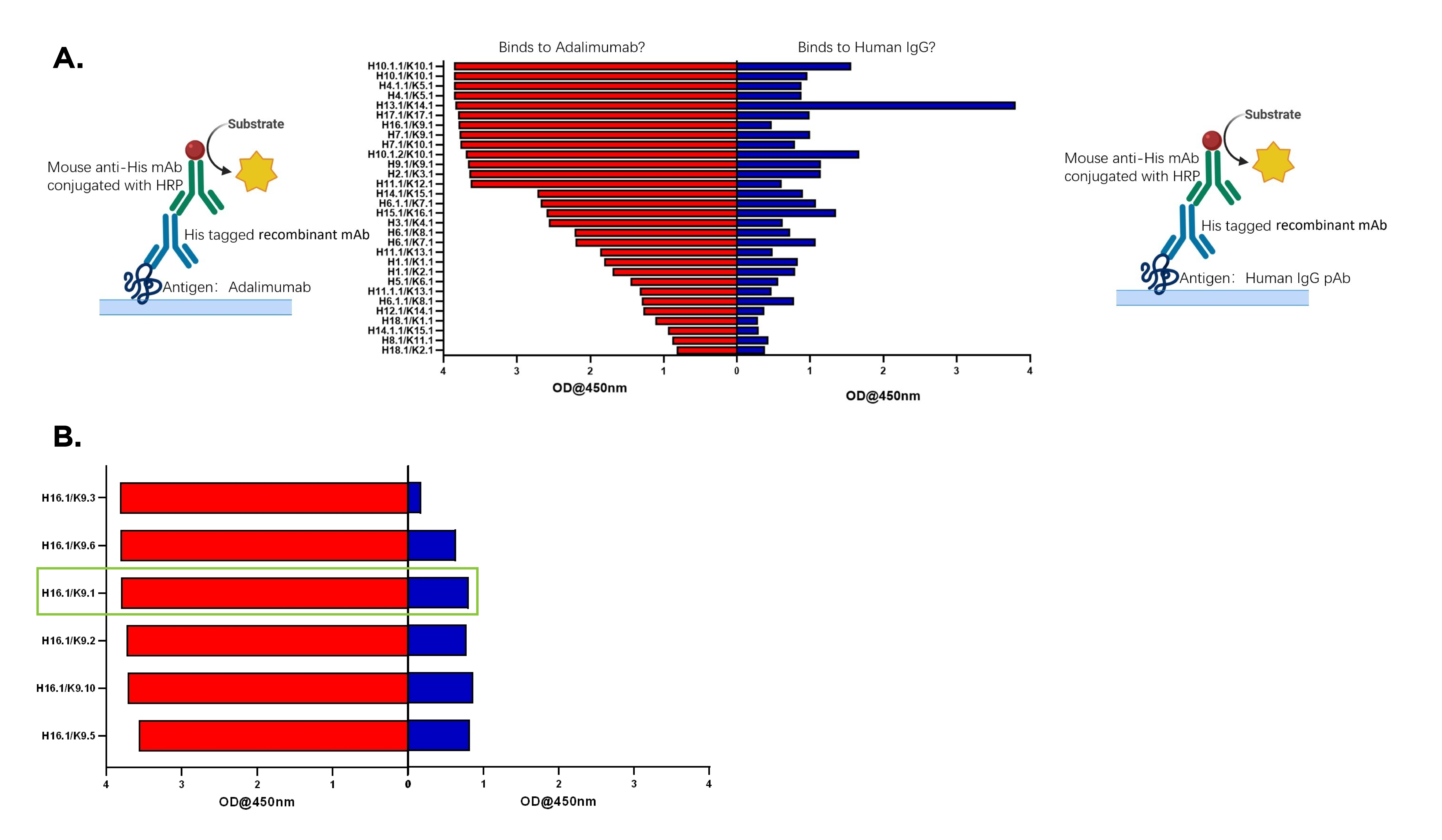
Figure 4: Recombinant antibody ELISA characterization. Fig. 4A shows the binding affinity of 30 identified anti-adalimumab recombinant sequences against adalimumab (target) and human IgG (off-target), alongside a schematic of the assay principle. Fig. 4B presents the binding profiles of heavy chain 16 paired with five alternate kappa light chains. The original pairing, H16.1/K9.1 (boxed in green), is compared to alternative combinations. Both panels demonstrate higher specificity for adalimumab over human IgG and illustrate how alternative light chain pairings can maintain target specificity and reduce off-target binding.
Conclusion
- Our strategic enrichment workflow selectively isolates functional anti-idiotypes prior to sequencing, significantly narrowing the candidate pool and improving discovery efficiency.
- This approach enables the identification of both blocking (type 1) and non-blocking (type 2) anti-idiotypes through integrated proteomic analysis and pre-selection strategies.
- Differential heavy-light chain pairing can preserve target specificity while minimizing off-target interactions.
More Information on REpAb® Antibody Discovery
Antibody Discovery Services
A mass spectrometry-based antibody discovery platform that enables functional selection through protein enrichment and purification strategies, and de novo sequences full-length antibodies from serum or purified protein samples.
Explore Antibody Discovery Services
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 10,000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and developed the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 9000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics