Yin, T., Ramon, A., Greenig, M., Sormanni, P., D’Adamio, L. Development of potent humanized TNFα inhibitory nanobodies for therapeutic applications in TNFα-mediated diseases. mAbs 17, 1 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2025.2498164
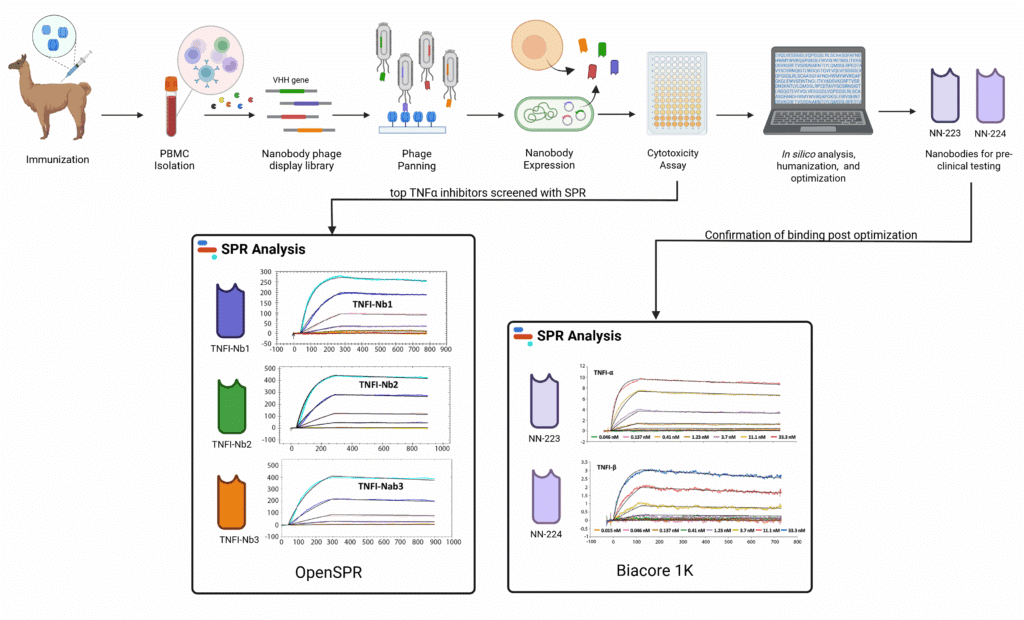
Researchers at Rutgers University developed TNFɑ inhibitory (TNFI) nanobodies isolated from camelids. SPR analysis was performed on the top 3 TNFI nanobodies. In silico analysis determined TNFI-Nb1 to be the most promising wild-type and was used to generate the NN-223 and NN-224 nanobodies.
Key Takeaways
- Engineered nanobodies like NN-223 and NN-224 represent promising developments in TNFα inhibitory therapeutics, addressing the common issues seen with larger, Fc-containing mAbs.
- Rapid Novor’s SPR binding kinetics service was used to assess the kinetic profiles of TNFα inhibitory nanobodies at multiple stages of the engineering process.
- Notably, the researchers were able to confirm that their nanobodies were able to maintain strong affinities for TNFα after optimization and humanization.
Summary
While current tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα)-targeting therapies effectively treat peripheral inflammatory diseases, their limited ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier reduces their efficacy in treating diseases of the central nervous system. Nanobodies offer an attractive alternative to traditional monoclonal antibody-based therapeutics because of their smaller size, ability to be further engineered for innovative drug delivery strategies, and lack of Fc-mediated immune activation.
In this study, Tao Yin, Aubin Ramon, and colleagues from Rutgers University and the University of Cambridge aimed to develop TNFα inhibitory (TNFI) nanobodies for pre-clinical development. The researchers isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from camelids immunized with human TNFα and used the VHH-encoding cDNA for phage display. In-silico analysis and machine-guided mutagenesis was then used to humanize and optimize the solubility of their top-performing nanobodies.
Using Rapid Novor’s SPR analysis service, the researchers were able to determine the binding kinetics of their nanobodies against TNFα, before and after humanization and optimization. SPR confirmed that their nanobodies maintained strong binding affinity to TNFα. This demonstrated that introducing mutations to the framework regions of antibodies, specifically to solvent-exposed residues, is a viable strategy for humanization without compromising binding-specificity.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 10,000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and developed the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 9000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics